Blog
How to Use Autodesk Maya: Beginner to Advanced Guide

Introduction to Autodesk Maya
Autodesk Maya is one of the most powerful 3D animation, modeling, and visual effects software used by professionals in film, TV, game development, and digital media. Known for its flexibility, robust toolset, and industry-standard capabilities, Maya enables users to create complex 3D models, stunning animations, realistic simulations, and photorealistic renderings.
Whether you are a beginner starting your first 3D project or an advanced user developing cinematic-quality visual effects, understanding Maya’s interface, tools, and workflow is essential for efficient and creative output. This guide will take you from beginner basics to advanced techniques, helping you master Autodesk Maya step by step.
Maya supports all aspects of 3D creation, including polygon modeling, NURBS, sculpting, rigging, animation, dynamics, simulation, and rendering. It integrates seamlessly with other Autodesk products and third-party tools like Adobe After Effects, Unity, and Unreal Engine.
Key Features of Autodesk Maya
1. 3D Modeling Tools
Autodesk Maya offers a comprehensive set of 3D modeling tools that cater to both beginners and professionals. Users can create polygon, NURBS, and subdivision surface models, allowing flexibility for low-poly game models or high-poly cinematic assets. Advanced sculpting tools make it easy to design complex organic shapes such as characters, creatures, and environments, as well as precise hard surface models for mechanical parts and architecture. These modeling capabilities ensure that artists can bring their creative ideas to life with precision and efficiency.
2. Animation & Rigging
Maya provides industry-standard animation tools for keyframe animation, motion paths, and constraints, enabling smooth and realistic movement for characters and objects. Its rigging tools allow the creation of detailed skeletons, inverse kinematics (IK) and forward kinematics (FK) setups, and blend shapes for facial expressions. Animators can build flexible rigs for characters, creatures, or machinery, making Maya ideal for films, games, and simulations where realistic movement is critical.
3. Dynamics & Simulation
Autodesk Maya excels at creating realistic physics-based simulations. Users can work with particle systems, nCloth, nHair, and fluid simulation to produce natural-looking effects such as flowing hair, realistic clothing, smoke, fire, water, and explosions. These dynamics tools help artists simulate real-world behaviors, adding depth and believability to animated scenes, whether for VFX, movies, or interactive applications.
4. Rendering
Maya comes integrated with the Arnold renderer, enabling photorealistic rendering directly within the software. It supports both GPU and CPU rendering pipelines, providing flexibility depending on hardware capabilities and project requirements. Artists can produce high-quality images, animations, and cinematic sequences without needing external rendering software, saving time and improving workflow efficiency.
5. UV Mapping & Texturing
Autodesk Maya offers robust UV unwrapping and texture painting tools, allowing precise control over how textures are applied to 3D models. It integrates seamlessly with Substance Painter and Adobe Photoshop, enabling artists to create detailed textures, materials, and surface finishes. This ensures that models are fully ready for rendering or export to game engines.
6. Scripting & Automation
Maya supports MEL and Python scripting, empowering users to automate repetitive tasks and customize workflows. Artists can create custom tools, user interfaces, and scripts, increasing efficiency for large-scale projects. Automation reduces manual effort, ensures consistency, and allows teams to focus on creative work rather than repetitive technical processes.
7. Pipeline Integration
Maya is designed for seamless integration within professional production pipelines. It is fully compatible with game engines like Unity and Unreal Engine, allowing direct export of assets for real-time applications. Maya also interoperates with other Autodesk products such as 3ds Max and MotionBuilder, enabling smooth collaboration across departments in large-scale film, animation, and game projects.
Uses of Autodesk Maya
1. Film & Television
Autodesk Maya is widely used in the film and television industry to create high-quality visual effects (VFX), character animation, and computer-generated environments. Studios rely on Maya for modeling realistic characters, animating complex movements, and simulating effects such as explosions, smoke, fire, and fluids. Its advanced rigging, animation, and rendering tools make it a standard choice for blockbuster movies, animated films, and TV series, where realism and cinematic quality are essential.
2. Video Games
In the video game industry, Autodesk Maya is used to model characters, props, environments, and in-game animations. Artists create both low-poly and high-detail assets optimized for real-time rendering. Maya’s seamless integration with game engines like Unity and Unreal Engine allows smooth asset transfer, rigging, and animation, helping developers build immersive and interactive gaming experiences efficiently.
3. Virtual Reality (VR) & Augmented Reality (AR)
Maya plays a key role in developing 3D assets for virtual reality and augmented reality applications. Designers use it to create realistic environments, interactive objects, and animated characters for immersive experiences. Maya’s precision modeling and animation tools help ensure that VR and AR content feels natural and responsive, enhancing user engagement across training simulations, virtual tours, and interactive experiences.
4. Advertising & Marketing
In advertising and marketing, Autodesk Maya is used to produce high-quality 3D visuals, animations, and product renderings. Brands use Maya to showcase products with realistic materials, lighting, and motion, creating compelling promotional content for commercials, digital ads, and social media campaigns. These visually rich assets help capture attention and communicate product value effectively.
5. Simulation & Education
Autodesk Maya is also widely used in education and training environments. Institutions use it to teach 3D modeling, animation principles, physics simulations, and visual storytelling. Maya is applied in simulations for engineering, medical visualization, and scientific research, helping students and professionals understand complex concepts through interactive 3D representations.
Benefits of Using Autodesk Maya
1. Industry Standard
Autodesk Maya is recognized as an industry-standard 3D software, trusted by leading Hollywood film studios, television production houses, and AAA game developers worldwide. Its widespread adoption means artists trained in Maya have strong career opportunities, as many professional pipelines are built around it. Using Maya ensures compatibility with established industry workflows and production standards.
2. Comprehensive Toolset
One of Maya’s biggest strengths is its all-in-one toolset. It combines powerful tools for 3D modeling, animation, rigging, dynamics, simulation, texturing, and rendering within a single application. This eliminates the need to rely on multiple software solutions, streamlining workflows and improving productivity for individuals and large teams alike.
3. Flexibility & Customization
Autodesk Maya offers exceptional flexibility and customization through its scriptable interface. With support for MEL and Python scripting, users can automate repetitive tasks, build custom tools, and tailor the interface to suit their workflow. This adaptability makes Maya suitable for small studios as well as complex, enterprise-level production pipelines.
4. High-Quality Output
Maya supports photorealistic rendering and cinematic-quality visual effects, especially through its integrated Arnold renderer. Artists can create highly detailed models, realistic lighting, and lifelike animations that meet the demanding quality standards of films, television, and high-end games.
5. Cross-Platform Integration
Autodesk Maya integrates seamlessly with other software and production pipelines. It works smoothly with game engines like Unity and Unreal Engine, texturing tools like Substance Painter, and other Autodesk products such as 3ds Max and MotionBuilder. This interoperability ensures efficient collaboration and smooth asset transfer across different stages of production.
Types / Versions of Autodesk Maya
1. Maya Standard
Maya Standard is the full professional version of Autodesk Maya and is widely used across film, television, VFX, and game development industries. It includes comprehensive tools for 3D modeling, sculpting, animation, rigging, dynamics, simulation, and rendering. This version is ideal for studios and professionals who require advanced features, flexible workflows, and integration with industry pipelines. Maya Standard supports high-end production needs, making it suitable for cinematic animation, visual effects, and complex 3D projects.
2. Maya LT
Maya LT is a lightweight version of Autodesk Maya designed specifically for indie game developers and small studios. It focuses on essential tools for 3D modeling, animation, and asset creation while excluding some advanced features like complex simulations. Maya LT offers a streamlined interface and lower system requirements, making it cost-effective and accessible for game developers who need professional-quality assets optimized for real-time engines such as Unity and Unreal Engine.
3. Maya with Arnold Renderer
This version of Autodesk Maya includes the Arnold renderer, a powerful, production-grade rendering engine used for photorealistic visuals and cinematic-quality output. Arnold enables realistic lighting, shading, and rendering directly within Maya, supporting both CPU and GPU rendering. This version is ideal for artists and studios focused on high-quality rendering for films, advertisements, and visual effects without relying on third-party renderers.
4. Educational Version
The Educational Version of Autodesk Maya provides free access to students, educators, and educational institutions. It includes all core features of the full professional version, allowing users to learn industry-standard workflows without limitations. This version is widely used in universities and training centers to teach 3D modeling, animation, rendering, and simulation, helping students build job-ready skills.
Getting Started with Autodesk Maya: Beginner Guide
1. Installing and Setting Up Maya
To begin using Autodesk Maya, download the software directly from Autodesk or through authorized resellers such as eSoftwareStore, which often provide guidance on licensing and activation. Before installation, ensure your system meets the minimum recommended requirements, including a high-performance GPU, a multi-core CPU, 16 GB or more RAM, and an SSD for faster loading and smoother performance. Once installed, activate Maya by signing in with your Autodesk account, which links your subscription or educational license to the software.
2. Maya User Interface Overview
The Maya interface is designed to support complex 3D workflows. The Main Menu provides access to tools for modeling, animation, rendering, and dynamics. The Channel Box and Layer Editor allow you to view and edit object transformations and manage display layers. The Outliner lists every object in the scene, making scene organization easy. The Viewport displays a real-time preview of your 3D scene, while the Attribute Editor lets you fine-tune object properties, materials, and modifiers.
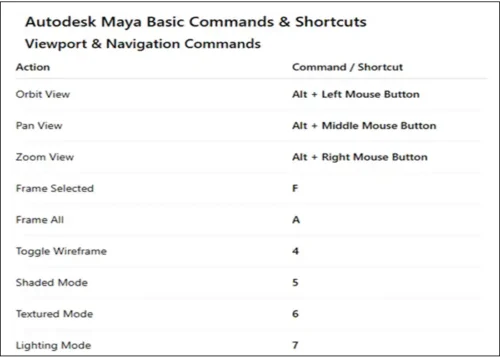
3. Basic Navigation
Navigating the 3D workspace efficiently is essential. Maya uses intuitive mouse shortcuts:
-
Orbit: Alt + Left Mouse Button rotates the camera around objects.
-
Pan: Alt + Middle Mouse Button moves the camera horizontally or vertically.
-
Zoom: Alt + Right Mouse Button zooms in and out of the scene.
Mastering these controls helps you work faster and more precisely.
4. Basic Modeling
Beginners typically start by creating primitive objects such as cubes, spheres, and cylinders. These shapes form the foundation of most models. You can move (W), rotate (E), and scale (R) objects to position them correctly. Tools like Extrude and Merge allow you to add detail and transform simple primitives into complex 3D shapes.
5. Basic Animation
Maya’s animation workflow is straightforward for beginners. To animate an object, select it and press S to set keyframes. Use the Graph Editor to refine motion curves for smoother animations. Constraints can be applied to control object relationships, making it easier to create realistic and complex movements.
Advanced Guide for Maya Users
1. Advanced Modeling Techniques
Advanced Maya users rely heavily on polygon modeling techniques to create clean, efficient, and production-ready assets. Tools such as edge loops, bevels, and insert edge loops help define sharp details and smooth transitions while maintaining proper topology. Topology optimization ensures clean edge flow, which is critical for deformation during animation.
For projects requiring smooth and mathematically precise surfaces, NURBS modeling is used to create clean curves and surfaces, commonly applied in product design and mechanical modeling. Retopology tools allow artists to convert high-resolution sculpted models into optimized, game-ready meshes, ensuring better performance while preserving visual quality.
2. Character Rigging
Character rigging is a core strength of Maya. Artists begin by building skeletons that define how characters move. Proper joint placement ensures natural motion and believable deformation. Inverse Kinematics (IK) and Forward Kinematics (FK) systems are used together to create flexible rigs for limbs, spines, and complex movement sequences.
For facial animation, blend shapes enable detailed expressions such as smiles, blinks, and speech movements. Combined with advanced skinning techniques, these tools allow characters to convey emotion and realism at a professional level.
3. Dynamics & Visual Effects
Maya’s dynamics tools enable realistic visual effects for high-end productions. Particle systems are used to create effects like explosions, sparks, smoke, and fire. nCloth simulates realistic cloth behavior for clothing, flags, and fabrics, responding naturally to motion and gravity.
Fluid containers simulate water, liquids, and gaseous effects, allowing artists to create believable splashes, waves, and flowing motion for cinematic scenes and simulations.
4. Advanced Rendering
Advanced rendering in Maya involves creating professional lighting setups using HDRI environments, area lights, and spotlights to achieve realistic illumination. The integrated Arnold renderer provides high-quality shading, accurate shadows, and physically based lighting.
Artists also use render passes and AOVs to separate lighting, shadows, reflections, and textures, making compositing easier in tools like After Effects or Nuke.
5. Scripting & Automation
For large or repetitive projects, Python scripting helps automate tasks such as scene cleanup, asset management, and batch operations. MEL scripts allow deep customization of Maya tools and workflows.
Batch rendering automation is essential for handling large animation projects efficiently, enabling studios to render multiple scenes or frames automatically, saving time and reducing errors.
Subscription Duration Options for Autodesk Maya
Autodesk Maya is available exclusively through a subscription-based licensing model, allowing individuals, freelancers, and studios to choose a plan that best fits their workflow, budget, and project duration. Autodesk offers three primary subscription duration options, each designed for different usage needs.
Monthly Subscription
The monthly subscription is ideal for short-term users, freelancers, or professionals working on a single project or temporary assignment. This option provides maximum flexibility, as users can start and stop their subscription without long-term commitment. It is particularly useful for testing Maya on real-world projects, handling peak workloads, or filling short production gaps. Since there is no long-term lock-in, teams can easily scale licenses up or down based on project demand.
Annual Subscription
The annual subscription is the most popular choice for regular users and professionals who rely on Maya as part of their daily workflow. Compared to paying monthly, this option is significantly more cost-effective over time, offering substantial savings across the year. It ensures uninterrupted access to all Maya features, updates, and technical support, making it ideal for animators, designers, and studios with continuous production schedules.
Multi-Year Subscription
The multi-year subscription, typically available for two or three years, is best suited for studios, enterprises, and long-term production environments. This option locks in pricing, protecting organizations from future price increases. It also simplifies budgeting and procurement while ensuring long-term software availability. Multi-year plans are ideal for companies focused on strategic planning, workforce stability, and large-scale creative pipelines.
FAQ About Autodesk Maya
Q1. Is Autodesk Maya suitable for beginners?
Yes, but it has a steep learning curve. Start with basic modeling and animation tutorials.
Q2. Can Maya be used for game development?
Absolutely, it’s widely used to create game characters, props, and animations.
Q3. Is Maya free?
Maya offers a 30-day free trial. Students and educators can access it for free.
Q4. What is the difference between Maya and Maya LT?
Maya LT is a lighter version with limited rendering and simulation tools, ideal for indie game developers.
Q5. Which industries use Maya?
Film, TV, gaming, VR/AR, advertising, education, and simulation industries.
Q6. Does Maya support rendering?
Yes, it comes with Arnold renderer and supports GPU/CPU rendering.
Q7. Can Maya integrate with Unity or Unreal Engine?
Yes, Maya assets can be exported in FBX format and imported into game engines.
Q8. What system requirements are needed for Maya?
High-performance GPU, multi-core CPU, 16GB+ RAM, SSD storage recommended.
Q9. Can I automate tasks in Maya?
Yes, using MEL or Python scripting.
Q10. Where can I buy Autodesk Maya?
From authorized resellers like eSoftwareStore or directly from Autodesk.
Conclusion
Autodesk Maya is a comprehensive 3D modeling, animation, and VFX software that serves beginners and advanced users alike. Its powerful tools for modeling, rigging, animation, dynamics, and rendering make it an essential choice for professionals in film, gaming, VR, and advertising. By learning Maya step-by-step—from basic modeling to advanced character rigging and simulations—you can create professional, industry-standard 3D content.
Maya’s versatility, combined with its integration with other Autodesk products, scripting capabilities, and pipeline compatibility, ensures it remains the leading solution for creative 3D professionals. For reliable licensing and professional support, purchase Autodesk Maya from eSoftwareStore, your trusted source for authentic Autodesk software.